Conflicts in Chemistry: The Case of Rare Earth Elements
Part of the Institute’s Conflicts in Chemistry role-playing simulation game series, The Case of Rare Earth Elements allows students to debate the positive and negative perspectives of rare earth elements from all sides, from producers and activists to manufacturers and consumers.
Rare earth elements are all around us, powering our phones, our cars, and scores of other technologies. Yet the mining and distribution of these elements have created challenges—environmental pollution, geopolitical monopolies, and threats to future sustainability—that must be addressed.
The Case of Rare Earth Elements asks you to consider the positive and negative aspects of rare earth elements through research and debate that explores the science, history, and controversies surrounding rare earth elements. The game is designed to take one to two weeks of classroom time.
Game Scenario
Leaders and experts from across the globe have come together at an international Sustainability Summit to develop a Sustainability Seal regarding rare earth elements. A Stewardship Council (the “Stewards”) has drafted a Statement of Guiding Values for this seal and have asked experts in the field of rare earth elements to provide comments, suggestions, and feedback for the Sustainability Seal. You will be playing either one of the Stewards or one of the invited experts, each with a strong and researched view about rare earth elements and about what should and should not be included in the Sustainability Seal.
What Is a Sustainability Seal?
A Sustainability Seal is a special label that says a product has been made in ways that protect the natural environment and/or workers. Some sustainability seals are regulated by government, like the Dolphin Safe Tuna label and the Organic label for foods. Other sustainability seals are created by people working outside of government.
In this game, we call those people “stewards.” Producers and manufacturers who follow the guidelines can use the Sustainability Seal on their packaging and advertising, certifying that they meet ethical and sustainable standards. Since the 1980s, many non-governmental labels have been created, including Fair Trade Coffee, the Rainforest Alliance, and the Forest Stewardship Council.
Game Roles
Students take on the role of rare earth experts from a variety of backgrounds and perspectives to argue their case before the sustainability summit stewards. There are 30 possible roles, representing international experts, manufacturers and suppliers, inventors and innovators, and global activists.
How to Play
If you are one of the stakeholders attending the Summit, it is your goal to convince the Stewards that the guidelines for a Sustainability Seal should reflect your role’s position on rare earth elements. You will be working with a group of like-minded experts–your interest group–to develop the most convincing arguments possible.
First, you must learn as much as you can about your interest group’s positions so you can effectively argue for them. Then you will meet with your group to prepare answers to questions the Stewards might ask, arguments for your positions, and counterarguments to the positions the other groups will present. All of these arguments should be based on evidence from your research.
At the summit, each group will briefly present its position before responding to questions from the stewards. Each group will have the chance to respond to each question and to the other groups, so you must be prepared to explain not only your own position but also where you disagree with the positions of other groups.
After the Summit, you will develop your position into a more concrete list of recommended guidelines for the final sustainability seal. In the debate, you will present and argue for your group’s proposal. At the conclusion of the debate, the Stewards will select one group’s proposal to adopt as part of the official Sustainability Seal. Each interest group will be ranked based on how well its goals are represented in the final Sustainability Seal. You will receive points if your proposal is selected and points based on your group’s ranking.
If you are a Steward, it is your job to decide which group and which proposal is most persuasive. You must research carefully, ask thoughtful questions, and pay close attention throughout the game.
Note: In this game, some of the assigned roles represent individuals from many nations and cultures. When assuming those personas, it is important to be aware of and to avoid stereotypes and implicit biases as you choose how to interpret the roles. Encourage each other to practice empathy, remain respectful, and focus on the substance of the individual’s experience and arguments.
Game Resources
Prepare for your debate by watching a short video and reviewing the background materials listed below. They will help you understand the science and the history of rare earth elements, including their production, commercial use, and trade and the associated environmental concerns.

Student Journal
This downloadable PDF will help students keep track of their assignments.
Council Tracking Sheet
This downloadable PDF helps students track arguments and prepare responses during each stage of the debate.
Videos, Readings & Other Sources
A comprehensive list that includes a short video, assigned readings, and other sources needed for game play.

Statement of Guiding Values
A list of guiding principles drafted by the Stewardship Council regarding rare earth elements.
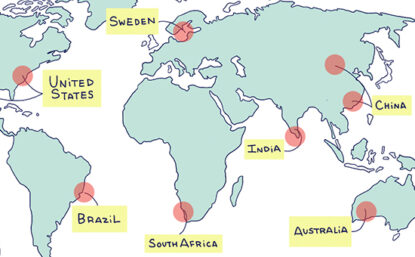
History and Future of Rare Earth Elements
The term rare earth was coined when an unusual black rock was unearthed by a miner in Ytterby, Sweden, in 1788.
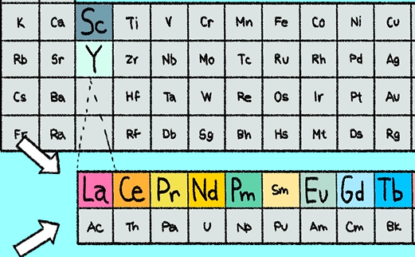
Science of Rare Earth Elements
The 17 metallic elements found in the middle of the periodic table have unique properties that make them essential to modern life.
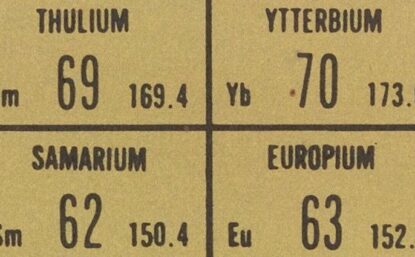
Featured image: Detail of series table of representative elements with supplementary tabulations for transitional and rare earth elements, 1957. Science History Institute.








